Class List
Here are the classes, structs, unions and interfaces with brief descriptions:
[detail level 12345]
| ▼Nhpp | Main namespace |
| ▼Nfcl | |
| ▼Ndetails | |
| CContactPoint | |
| ▼CEPA | Class for EPA algorithm |
| CSimplexF | |
| CSimplexHorizon | |
| CSimplexList | |
| ▼CGJK | Class for GJK algorithm |
| CSimplex | |
| CSimplexV | |
| CMinkowskiDiff | Minkowski difference class of two shapes |
| ▼Ninternal | |
| CLoader | |
| CTriangleAndVertices | |
| ▼Ntools | |
| ▼CProfiler | This is a simple thread-safe tool for counting time spent in various chunks of code. This is different from external profiling tools in that it allows the user to count time spent in various bits of code (sub-function granularity) or count how many times certain pieces of code are executed |
| CScopedBlock | This instance will call Profiler::begin() when constructed and Profiler::end() when it goes out of scope |
| CScopedStart | This instance will call Profiler::start() when constructed and Profiler::stop() when it goes out of scope. If the profiler was already started, this block's constructor and destructor take no action |
| CAABB | A class describing the AABB collision structure, which is a box in 3D space determined by two diagonal points |
| CBox | Center at zero point, axis aligned box |
| CBVFitter | The class for the default algorithm fitting a bounding volume to a set of points |
| CBVFitter< AABB > | Specification of BVFitter for AABB bounding volume |
| CBVFitter< kIOS > | Specification of BVFitter for kIOS bounding volume |
| CBVFitter< OBB > | Specification of BVFitter for OBB bounding volume |
| CBVFitter< OBBRSS > | Specification of BVFitter for OBBRSS bounding volume |
| CBVFitter< RSS > | Specification of BVFitter for RSS bounding volume |
| CBVFitterTpl | The class for the default algorithm fitting a bounding volume to a set of points |
| CBVHFrontNode | Front list acceleration for collision Front list is a set of internal and leaf nodes in the BVTT hierarchy, where the traversal terminates while performing a query during a given time instance. The front list reflects the subset of a BVTT that is traversed for that particular proximity query |
| CBVHModel | A class describing the bounding hierarchy of a mesh model or a point cloud model (which is viewed as a degraded version of mesh) |
| CBVHModelBase | A base class describing the bounding hierarchy of a mesh model or a point cloud model (which is viewed as a degraded version of mesh) |
| CBVNode | A class describing a bounding volume node. It includes the tree structure providing in BVNodeBase and also the geometry data provided in BV template parameter |
| CBVNodeBase | BVNodeBase encodes the tree structure for BVH |
| CBVSplitter | A class describing the split rule that splits each BV node |
| ▼CCachedMeshLoader | |
| CKey | |
| CCapsule | Capsule It is 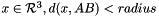 where where 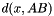 is the distance between the point x and the capsule segment AB, with is the distance between the point x and the capsule segment AB, with 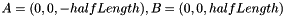 |
| CCollisionFunctionMatrix | Collision matrix stores the functions for collision between different types of objects and provides a uniform call interface |
| CCollisionGeometry | The geometry for the object for collision or distance computation |
| CCollisionObject | Object for collision or distance computation, contains the geometry and the transform information |
| CCollisionRequest | Request to the collision algorithm |
| CCollisionResult | Collision result |
| CCone | Cone The base of the cone is at 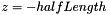 and the top is at and the top is at 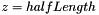 |
| CContact | Contact information returned by collision |
| CConvex | Convex polytope |
| ▼CConvexBase | Base for convex polytope |
| CNeighbors | |
| CCylinder | Cylinder along Z axis. The cylinder is defined at its centroid |
| CDistanceFunctionMatrix | Distance matrix stores the functions for distance between different types of objects and provides a uniform call interface |
| CDistanceRequest | Request to the distance computation |
| CDistanceResult | Distance result |
| CGJKSolver | Collision and distance solver based on GJK algorithm implemented in fcl (rewritten the code from the GJK in bullet) |
| CHalfspace | Half Space: this is equivalent to the Plane in ODE. The separation plane is defined as n * x = d; Points in the negative side of the separation plane (i.e. {x | n * x < d}) are inside the half space and points in the positive side of the separation plane (i.e. {x | n * x > d}) are outside the half space |
| CKDOP | KDOP class describes the KDOP collision structures. K is set as the template parameter, which should be 16, 18, or 24 The KDOP structure is defined by some pairs of parallel planes defined by some axes. For K = 16, the planes are 6 AABB planes and 10 diagonal planes that cut off some space of the edges: (-1,0,0) and (1,0,0) -> indices 0 and 8 (0,-1,0) and (0,1,0) -> indices 1 and 9 (0,0,-1) and (0,0,1) -> indices 2 and 10 (-1,-1,0) and (1,1,0) -> indices 3 and 11 (-1,0,-1) and (1,0,1) -> indices 4 and 12 (0,-1,-1) and (0,1,1) -> indices 5 and 13 (-1,1,0) and (1,-1,0) -> indices 6 and 14 (-1,0,1) and (1,0,-1) -> indices 7 and 15 For K = 18, the planes are 6 AABB planes and 12 diagonal planes that cut off some space of the edges: (-1,0,0) and (1,0,0) -> indices 0 and 9 (0,-1,0) and (0,1,0) -> indices 1 and 10 (0,0,-1) and (0,0,1) -> indices 2 and 11 (-1,-1,0) and (1,1,0) -> indices 3 and 12 (-1,0,-1) and (1,0,1) -> indices 4 and 13 (0,-1,-1) and (0,1,1) -> indices 5 and 14 (-1,1,0) and (1,-1,0) -> indices 6 and 15 (-1,0,1) and (1,0,-1) -> indices 7 and 16 (0,-1,1) and (0,1,-1) -> indices 8 and 17 For K = 18, the planes are 6 AABB planes and 18 diagonal planes that cut off some space of the edges: (-1,0,0) and (1,0,0) -> indices 0 and 12 (0,-1,0) and (0,1,0) -> indices 1 and 13 (0,0,-1) and (0,0,1) -> indices 2 and 14 (-1,-1,0) and (1,1,0) -> indices 3 and 15 (-1,0,-1) and (1,0,1) -> indices 4 and 16 (0,-1,-1) and (0,1,1) -> indices 5 and 17 (-1,1,0) and (1,-1,0) -> indices 6 and 18 (-1,0,1) and (1,0,-1) -> indices 7 and 19 (0,-1,1) and (0,1,-1) -> indices 8 and 20 (-1, -1, 1) and (1, 1, -1) –> indices 9 and 21 (-1, 1, -1) and (1, -1, 1) –> indices 10 and 22 (1, -1, -1) and (-1, 1, 1) –> indices 11 and 23 |
| CkIOS | A class describing the kIOS collision structure, which is a set of spheres |
| CMeshLoader | |
| COBB | Oriented bounding box class |
| COBBRSS | Class merging the OBB and RSS, can handle collision and distance simultaneously |
| COcTree | Octree is one type of collision geometry which can encode uncertainty information in the sensor data |
| CPlane | Infinite plane |
| CRSS | A class for rectangle sphere-swept bounding volume |
| CShapeBase | Base class for all basic geometric shapes |
| CSphere | Center at zero point sphere |
| CTransform3f | Simple transform class used locally by InterpMotion |
| CTraversalTraitsCollision | |
| CTraversalTraitsDistance | |
| CTriangle | Triangle with 3 indices for points |
| CTriangleP | Triangle stores the points instead of only indices of points |
| CMeshShapeDistanceTraversalNodekIOS | |
| CMeshShapeDistanceTraversalNodeOBBRSS | |
| CMeshShapeDistanceTraversalNodeRSS | Traversal node for distance between mesh and shape, when mesh BVH is one of the oriented node (RSS, kIOS, OBBRSS) |
| CShapeMeshDistanceTraversalNode | Traversal node for distance between shape and mesh |
| CShapeMeshDistanceTraversalNodekIOS | |
| CShapeMeshDistanceTraversalNodeOBBRSS | |
| CShapeMeshDistanceTraversalNodeRSS | Traversal node for distance between shape and mesh, when mesh BVH is one of the oriented node (RSS, kIOS, OBBRSS) |
